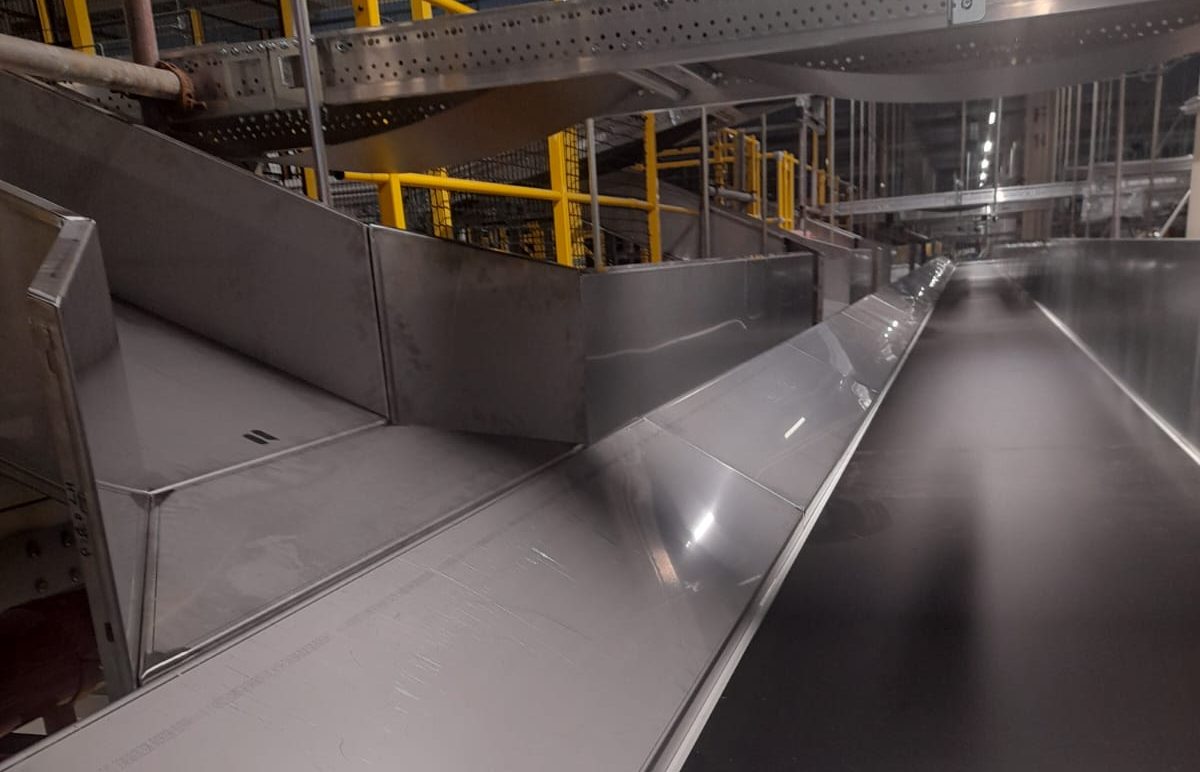
Structures and Mezzanine Installation
Installing structures and mezzanines in commercial or industrial settings typically starts with careful planning and engineering. This includes assessing the available space, load-bearing capacity of the existing floor, and the intended use of the mezzanine or structure. The installation process generally includes tasks such as:
1) Site Assessment: Evaluating the space to determine the most suitable location for the mezzanine or structure.
2) Design and Engineering: Developing detailed plans and structural engineering calculations to ensure safety and compliance with local building codes.
3) Permitting: Obtaining necessary permits and approvals from local authorities before construction begins.
4) Foundation and Support Structure Installation: Preparing the site by installing supporting columns, beams, and footings, which provide the structural integrity for the mezzanine.
5) Assembly: Assembling the mezzanine or structure components, including the flooring, handrails, and access points.
6) Safety Features: Installing safety features such as guardrails, staircases, and fire protection systems to meet safety regulations.
7) Utilities: If required, integrating utilities such as electrical wiring, lighting, HVAC, or plumbing into the mezzanine or structure.
8) Quality Control: Conducting quality checks and inspections to ensure structural stability and safety.
9) Final Inspection: Completing a final inspection to ensure that the installation meets all building codes and safety standards.
10) Handover: Handing over the installed mezzanine or structure to the client or end-user, along with any necessary documentation and maintenance guidelines.
Effective installation of structures and mezzanines is essential for maximizing space utilization in industrial and commercial settings while ensuring the safety and functionality of the newly created areas. Proper planning and adherence to building codes and safety standards are crucial throughout the installation process.